Best Practices for Terraform Infrastructure
In this document, we will explore the best practices for managing infrastructure as code using Terraform. Terraform is a powerful tool that allows you to define and provision your infrastructure using a declarative configuration language. By following these best practices, you can ensure that your Terraform configurations are maintainable, scalable, and secure.
Press enter or click to view image in full size
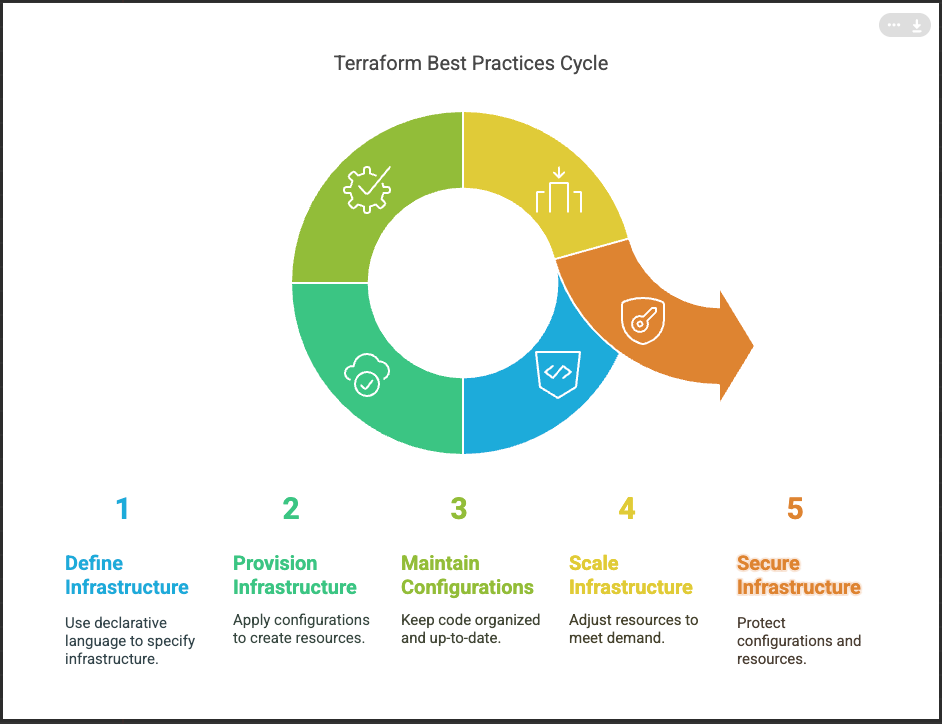
1. Use Version Control
Always store your Terraform configuration files in a version control system (VCS) like Git. This allows you to track changes, collaborate with team members, and roll back to previous versions if necessary.
2. Organize Your Code
Structure your Terraform code in a logical and organized manner. Use modules to encapsulate reusable components and keep your main configuration files clean. A common structure includes:
/terraform
/modules
/module1
/module2
/environments
/dev
/prod
main.tf
variables.tf
outputs.tf
3. Use Variables and Outputs
Define variables for any values that may change between environments or deployments. This makes your code more flexible and reusable. Additionally, use output values to expose important information about your infrastructure.
4. Keep State Files Secure
Terraform uses state files to keep track of the resources it manages. Ensure that these files are stored securely, preferably in a remote backend like AWS S3 with encryption enabled. Avoid storing state files in version control.
5. Use Remote Backends
Utilize remote backends for storing your Terraform state. This allows for better collaboration among team members and provides locking mechanisms to prevent concurrent modifications. Popular options include AWS S3, HashiCorp Consul, and Terraform Cloud.
6. Implement Workspaces
Use Terraform workspaces to manage different environments (e.g., development, staging, production) within the same configuration. This helps to isolate state files and manage resources more effectively.
7. Plan Before Applying
Always run terraform plan before applying changes. This command provides a preview of what changes will be made, allowing you to catch potential issues before they affect your infrastructure.
Press enter or click to view image in full size
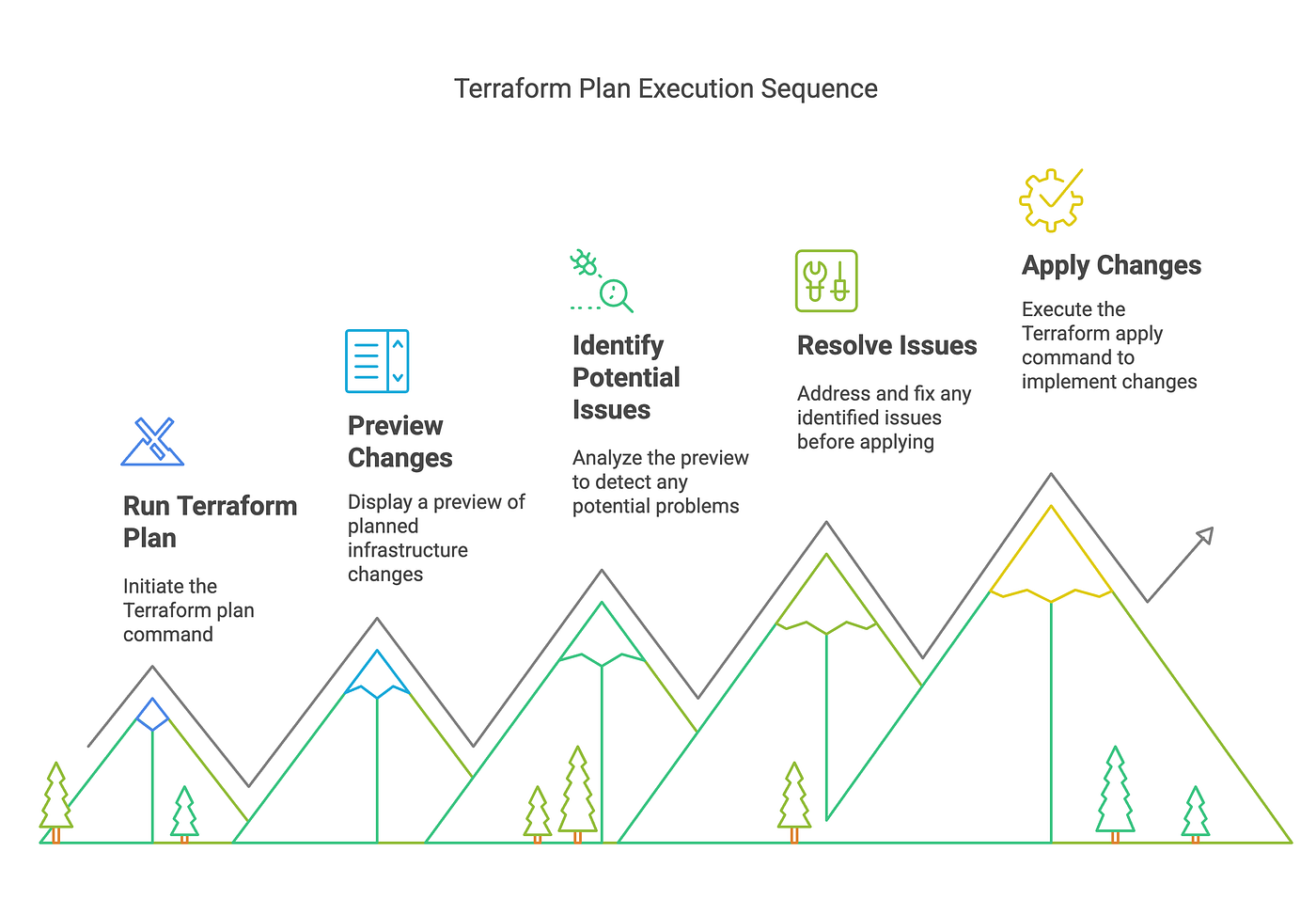
8. Use Terraform Modules
Leverage Terraform modules to promote code reuse and maintainability. Modules can encapsulate common patterns and configurations, making it easier to manage complex infrastructures.
9. Keep Your Providers Updated
Regularly update your provider versions to benefit from the latest features, bug fixes, and security patches. Use version constraints in your configuration to ensure compatibility.
10. Document Your Code
Add comments and documentation to your Terraform configurations. This helps other team members understand the purpose and functionality of your code, making it easier to maintain in the long run.
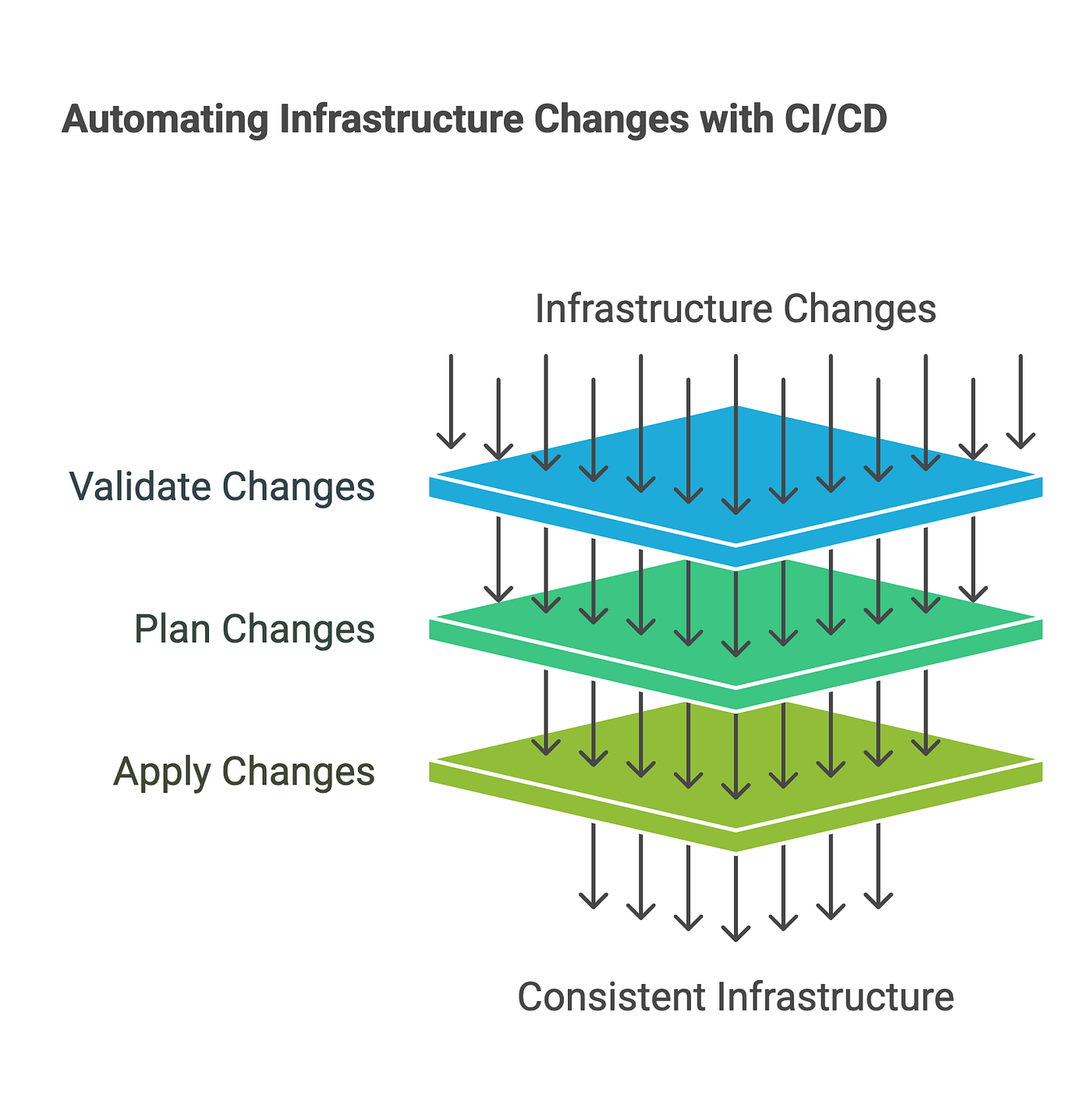
11. Implement CI/CD Pipelines
Integrate Terraform into your continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. Automate the process of validating, planning, and applying changes to your infrastructure, ensuring consistency and reducing manual errors.
Press enter or click to view image in full size
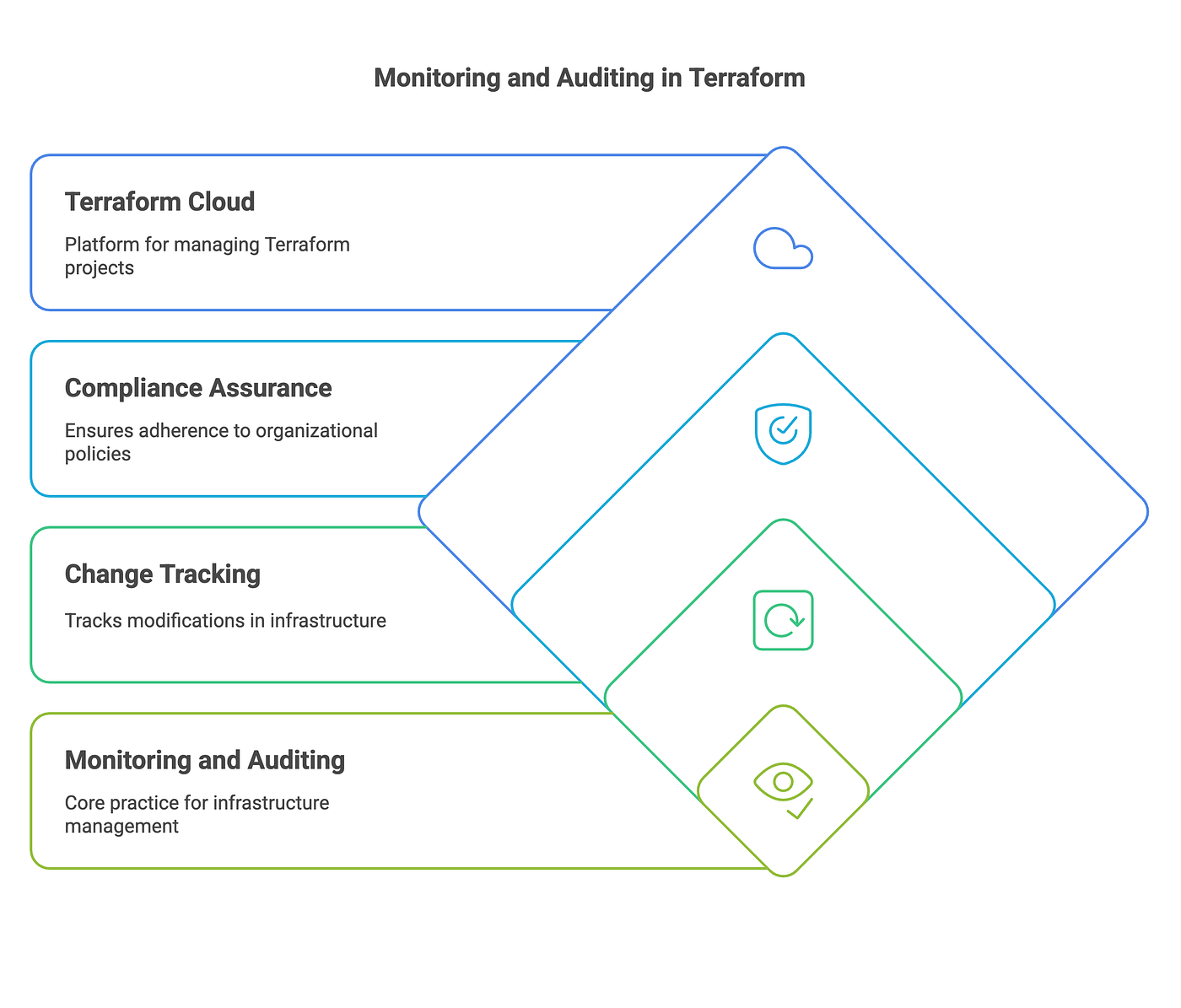
12. Monitor and Audit Changes
Implement monitoring and auditing for your Terraform-managed infrastructure. Use tools like Terraform Cloud or third-party solutions to track changes and ensure compliance with your organization’s policies.
Press enter or click to view image in full size
Conclusion
By adhering to these best practices, you can effectively manage your Terraform infrastructure, ensuring that it is secure, maintainable, and scalable. As you continue to work with Terraform, always seek to improve your processes and stay updated with the latest features and community recommendations.





